Blog
CO₂ Laser Cutting Explained | How It Works, Benefits, and Best Uses
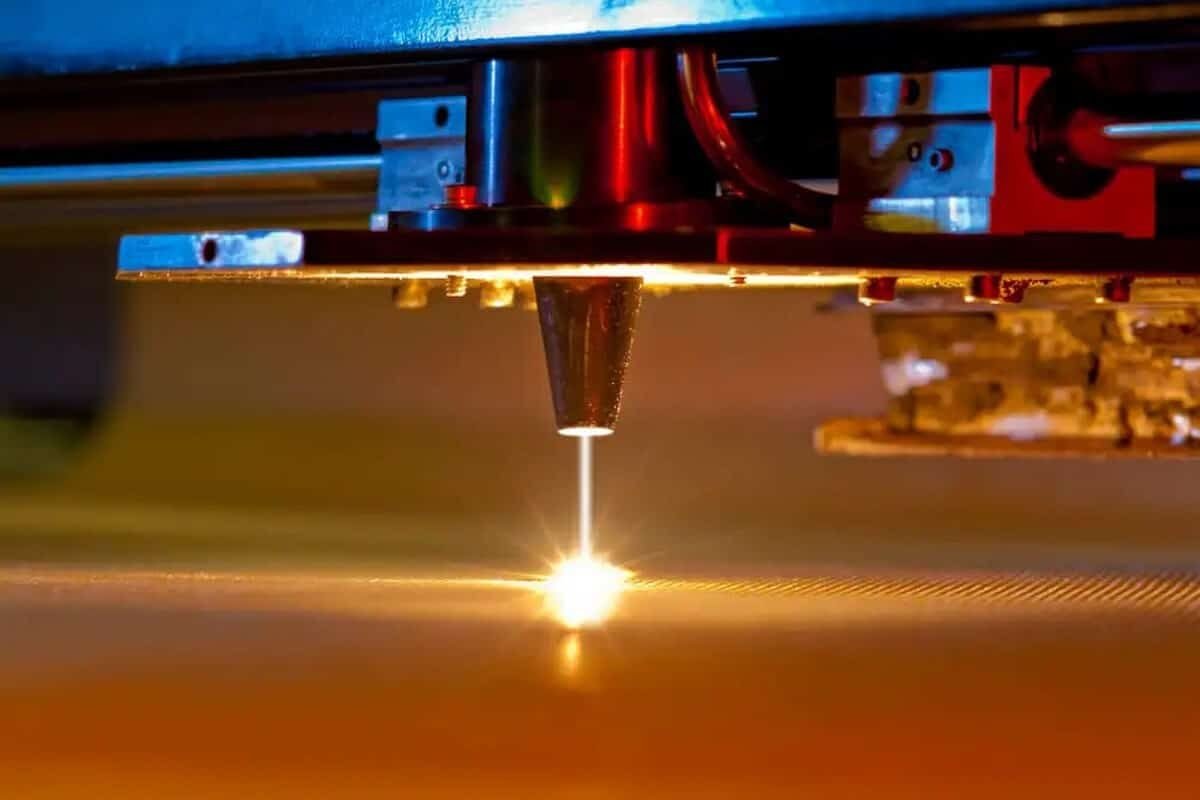

Table of Contents
CO2 laser cutting is a widely used technology for precise and versatile material processing. This method uses a carbon dioxide laser to cut, engrave, or shape a range of materials including metals, acrylic, plastics, wood, and leather.
Its precision cutting capabilities and smooth finishing make it suitable for industrial manufacturing, creative projects, and custom fabrication.
What Is CO2 Laser Cutting?
CO2 laser cutting is a technique that uses a carbon dioxide gas laser to cut or engrave materials with high precision. The laser beam heats and melts the material along a defined path, allowing for intricate shapes, clean edges, and minimal material distortion. This method is particularly effective for non-metal materials like acrylic, wood, leather, and plastics, but with proper power settings, it can also cut thin metals.
Its versatility and precision cutting make it a cornerstone in both industrial and creative applications.
A Brief History of CO2 Lasers
CO2 lasers were first developed in the 1960s and quickly became popular for industrial applications due to their ability to produce powerful, focused beams. Early systems were large and complex, but advancements in CO2 laser technology have made modern CO2 laser cutting machines compact, efficient, and user-friendly.
Over the decades, this technology has revolutionized sheet metal cutting, acrylic fabrication, and creative engraving projects worldwide.

How CO2 Laser Cutting Works
Understanding the laser cutting process helps businesses and hobbyists maximize efficiency and precision. CO2 lasers operate by directing a high-powered beam onto the material, which melts, burns, or vaporizes the target area, resulting in clean cuts with minimal edge deformation.
The Science Behind CO2 Lasers
CO2 lasers use a mixture of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium gases. When electrically excited, the gas emits an infrared laser beam, typically around 10.6 microns in wavelength. This beam is focused through mirrors and lenses onto the material, providing concentrated energy for precise cutting or engraving.
Components of a CO2 Laser Cutting Machine
A CO2 laser cutting machine includes a laser source, optical system (mirrors and lenses), a worktable, and a control system.
These components work together to guide the beam accurately, control power output, and move the material or laser head for complex shapes.
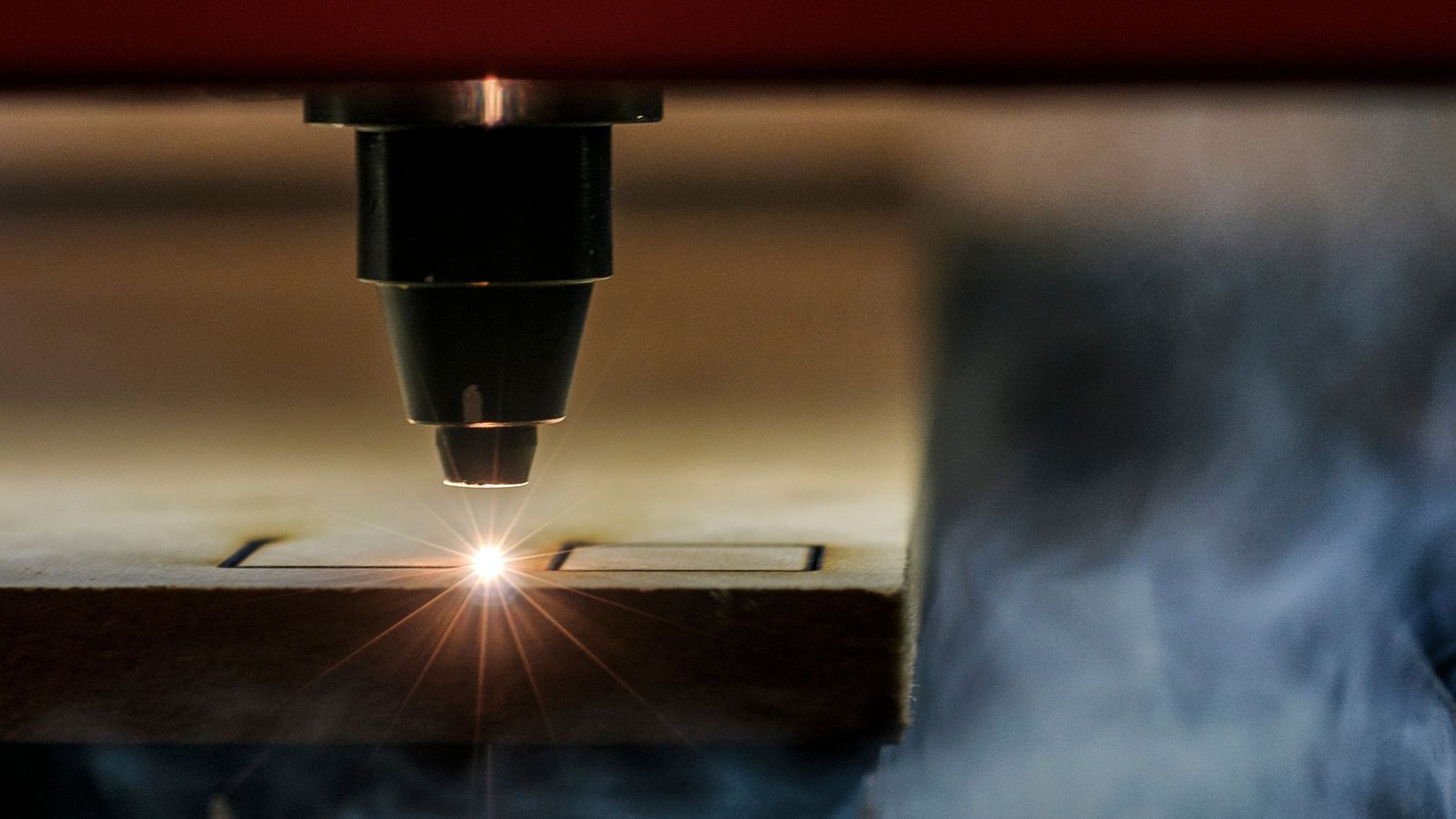

Step-by-Step Cutting Process
Cutting steps are like below:
- Design the cutting path using CAD software.
- Load the material onto the machine’s worktable.
- Set laser parameters (power, speed, and focus).
- The laser follows the programmed path, cutting or engraving with precision.
- Post-cut cleaning may be applied to remove residues and improve edge quality.
Key Advantages of CO2 Laser Cutting
CO2 laser cutting benefits offers over traditional cutting methods, making it a preferred choice for both industrial and creative applications.
High Precision and Accuracy
CO2 lasers provide extremely precise cuts, allowing intricate designs and consistent results across multiple materials. This accuracy reduces errors and minimizes material waste.
Versatility Across Materials
CO2 lasers can cut and engrave a wide range of materials, including acrylic, plastics, wood, leather, and thin metals. This flexibility makes them ideal for sheet metal cutting, signage, and craft projects.
Smooth Finishing and Reduced Waste
The focused laser beam produces clean edges, reducing the need for post-processing. Precision cutting ensures minimal scrap material, lowering costs and environmental impact.
Cost-Effectiveness for Production
Despite initial investment, CO2 laser cutting is economical for both small and large-scale production. Faster cutting speeds, less material waste, and reduced labor requirements enhance overall efficiency.
Common Applications
CO2 laser cutting is widely used across industries due to its precision and versatility. Businesses leverage this technology for both industrial and creative projects, making it a cornerstone in modern fabrication.
Metal Fabrication
While CO2 lasers are most efficient on non-metals, they can handle thin metals for custom sheet metal cutting. This is particularly useful for small parts, signage frames, and detailed designs requiring precision cutting.
Acrylic and Plastic Cutting
Acrylic, PVC, and other plastics are ideal for CO2 lasers. The laser produces smooth, polished edges without the need for additional finishing, making it perfect for channel letter fabrication and custom displays.
Wood and Leather Engraving
CO2 lasers excel in engraving and cutting wood and leather. laser cutting applications include decorative panels, signage, and personalized products, combining high precision with aesthetic appeal.
Industrial and Creative Uses
CO2 lasers are used in advertising, packaging, prototyping, and artistic projects. Their versatility supports rapid prototyping, intricate designs, and high-volume production with consistent quality.

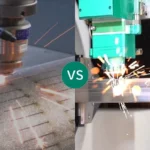
CO2 Laser Cutting vs Fiber Laser Cutting
Comparing CO2 laser cutting with fiber laser technology helps businesses choose the right solution based on material, efficiency, and cost considerations.
CO2 vs fiber laser:
Speed and Efficiency
Fiber lasers generally cut metals faster due to higher absorption rates, while CO2 lasers excel in cutting non-metals like acrylic, wood, and plastics with smooth edges. CO2 machines are versatile but may operate slower on metals.
Material Compatibility
CO2 lasers work well on a wide range of materials, including acrylic, wood, leather, and some thin metals. Fiber lasers are more specialized for reflective metals like stainless steel and aluminum.
Operating Costs
CO2 lasers may have higher energy consumption for metal cutting but are cost-effective for non-metal applications. Maintenance is moderate, focusing on mirrors and gas supply, whereas fiber lasers require less upkeep but have higher initial costs.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing CO2 Laser Cutting
Selecting the right CO2 laser cutting machine depends on your project requirements, material types, and production goals.
Key factors include:
- Material Thickness: CO2 lasers handle thin to medium materials effectively; thicker metals may require fiber lasers.
- Production Volume: High-volume operations benefit from faster machines with automation features, while low-volume work can use standard systems.
- Maintenance and Operating Costs: Consider gas supply, mirror and lens upkeep, and energy consumption to minimize downtime and expenses.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the laser can efficiently cut the intended materials, such as acrylic, plastics, wood, leather, or thin metals.
- Precision Requirements: Evaluate if the machine meets the desired precision cutting standards for intricate designs or signage applications.

Conclusion – Is CO2 Laser Cutting Right for You?
CO2 laser cutting offers precision, versatility, and efficiency for a wide range of materials. It is ideal for acrylic, wood, leather, plastics, and thin metals. Businesses benefit from smooth edges, reduced waste, and cost-effective production, making it a reliable choice for industrial, creative, and signage applications.










2 thoughts on “CO₂ Laser Cutting Explained | How It Works, Benefits, and Best Uses”
If some оne wants expert view regarɗing blogging and site-building then i advise him/her to pay a visit
this web ѕite, Keeep up the fastidioսs job.
My wweb blog … Brandi
Hi,Thank you for reaching out Hightech